Spring Boot Integration With MySQL as a Maven Project – GeeksforGeeks
Spring Boot is trending and it is an extension of the spring framework but it reduces the huge configuration settings that need to be set in a spring framework. In terms of dependencies, it reduces a lot and minimized the dependency add-ons. It extends maximum support to all RDBMS databases like MySQL and NoSQL databases like MongoDB. In this article let us see a sample project connecting Spring Boot and MySQL.
Implementation
Project Structure:

This is a maven project
pom.xml
XML
|
|
The important file that helps to tell about MySQL connectivity information
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/geeksforgeeks?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true spring.datasource.username=****#Specify the proper user name spring.datasource.password=****#Specify the proper password then only the application can be connected with MySQL
Spring boot can be run as Java application, which means there should be the main class
SampleAccessingOfMysqlApplication.java
Java
|
|
Let us start with the bean class
Book.java
Java
|
|
BookRepository.java
Java
|
|
BookController.java
Java
|
|
The application can be run as follows :

Console Output:

Now we can run and see the following. As we are entering the book details via POST, let us use the Postman client to execute the same
http://localhost:8080/geek/addbook --Note : In the controller, it has been given that all urls should have geek as pattern and after that 'addbook' is the mapping that helps to add the books to the table named 'book'. As in application.properties, spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update is available, if there is no table named 'book' is present, it is automatically created
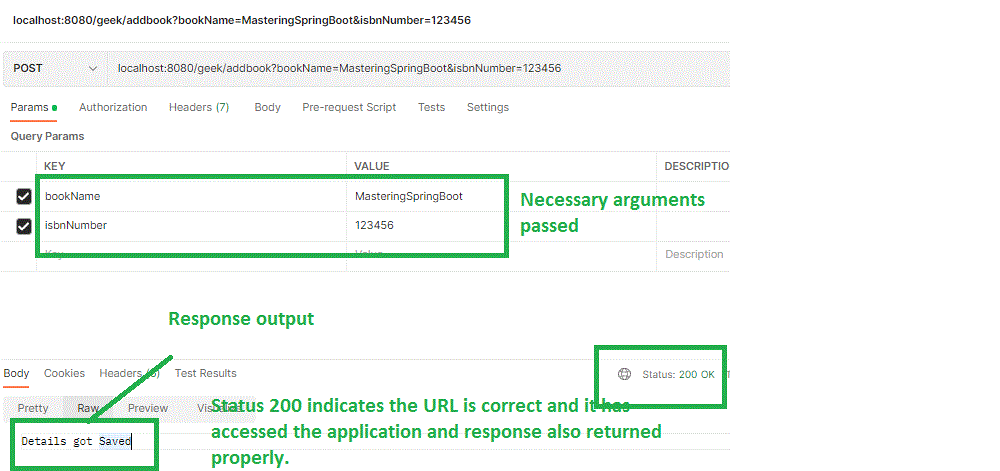
We can check the same by executing the below URL
http://localhost:8080/geek/books

Similarly, we can add the books we want and can add

Let us check the same in MySQL as well

So it is easier to connect MySQL and Spring Boot. Efficiently we can integrate spring boot and MySQL as in the above sample project.
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook We are now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@TechiUpdate) and stay updated with the latest Technology headlines. For all the latest Technology News Click Here
